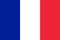
In children, the foot deformation is a pathology in which the distance between the inner side of the ankle is at least 4-5 cm, tightening and straightening the legs.At the same time, the heel, along with the fingers, differs to the outside, and it seems that the inner arches of the legs flood inward.
In orthopedics, this curvature of the legs is called x-shaped (on the contrary, O-shaped curvature is observed).If there is a decrease in the height of the leg arches in the background of the valgus deformation, it is said to be a flat-valgus deformation.
Generally, parents are noticeable due to deformation of the legs of children when they do seven to eight months, and during this period they have the first independent walk.If you look at a photo of a flat valley deformation of the legs, you can notice that the legs are leaning in the knee joints and the heel "looks up" and the distance between the legs is quite large, they are.
Classification
In medicine, the three -degree severity of the valgus anomaly is distinguished:
- Light.The height of the arch is less than 140 °, the longitudinal arc of the stop is approximately 15-20 mm and the back of the leg is approx.
- Average.Arc height is 150-160 ° in the second degree of deformation of the leg, 10 mm height, the height of the heel is 10 mm, the heel is 10 °, and the back of the leg and the front vault are up to 15 °.
- Heavy (foot circle).The height of the vault is between 0 and 5 mm, with the Calcaneus tilt angle between 0 and 5 °, the arc vault is above 160-180 °, the back section position and the front section of the front is over 20 °.The child complains of the continuous pain of the joint.The severe severity of deformation is not applicable to complete correction.
There is another classification of the valgus deformation of the legs based on the disease:

- Compensatory (caused by shortened Achilles).
- Structural (due to the congenital irregular position of the Aries bone).
- Spastic (a consequence of muscle cramps that occur due to abnormalities in the work of the cortex).
- Improvement hyper (illiterate treatment of children's curvature).
- Rachitic (manifested in children of Rick).
- Paralysis (encephalitis or polio complication).
- Traumatic (ankle joint bones, caused by fracture of the leagues).
Causes of Valgus deformation of the legs in children
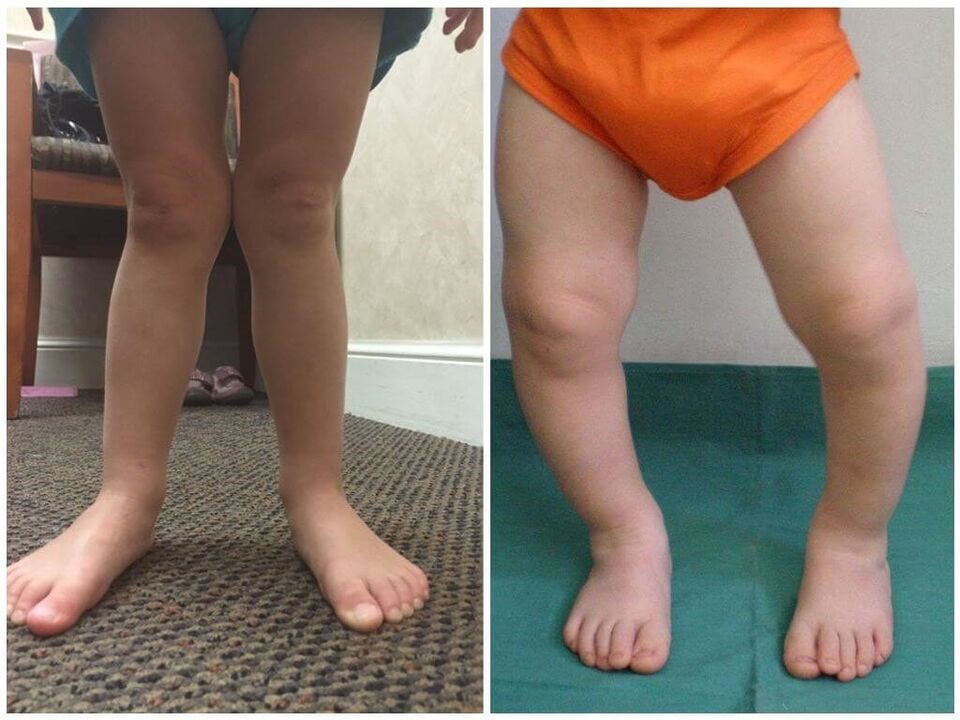
The deformation of the foot dose is congenital and acquired.In the first case, the causes of the disease are caused by intrauterine violation of the location/shape of the bones.The diagnosis is made in infancy.
The acquired form of the Valgus disorder is not caused by differences in the formation of the muscle bone system.Usually the diagnosis of the "valgus -deformation" is made by eight months of child or when a small patient is 1 year old.The difference is most often formed in weakened children with muscle hypotension.
In the child, among the most common causes of leg deformation:
- no supervision;
- intrauterine hypotropy;
- Common diseases of bronchitis, acute respiratory viral infections, pneumonia;
- Congenital weakness of connective tissues;
- Angle;
- Ligaments injuries, lower leg bones, muscles;
- Long stay in plaster;
- Obesity of children;
- Too early setting the child to the legs;
- Wearing poor quality/improperly selected shoes.
In addition, the Valgus disorder occurs:
- Brain paralysis;
- Polyneuropathy;
- osteoporosis;
- dysplasia;
- endocrine and genetic disorders;
- Congenital dislocation of the thigh;
- polio;
- Muscular dystrophia.
Symptoms of Valgus deformation
Symptoms of leg deformation in children are as follows:
- While walking, the child does not enter the entire foot, but only on the inside of the inside (the legs flooded inward).
- The legs get a x -shaped shape.
- Walking becomes unpleasant.
- The child complains of the pain of the legs.
- In the evenings, swelling of the legs is possible, cramps.
- The shoe that the child is wearing is unevenly - above all, the inside of the sole is worn out.
If you find similar symptoms on your own, see the doctor immediately.It is easier to prevent the disease than to deal with the consequences.
Diagnosis
In order to make a diagnosis such as Stop deformation, the doctor's traumatologist-ortopedist examines the child and prescribes a separate examination:
- podometre (the method evaluates the distribution of the load on certain departments of the legs);
- Computer planography (allows the morphological parameters of the legs to calculate);
- Radiography (allows you to study the leg change relative to each other).
In some cases, the joints require additional ultrasound.To exclude the relationship between the valgus deformation, the child is directed to the child neurologist with the diseases of the central/peripheral nervous system.
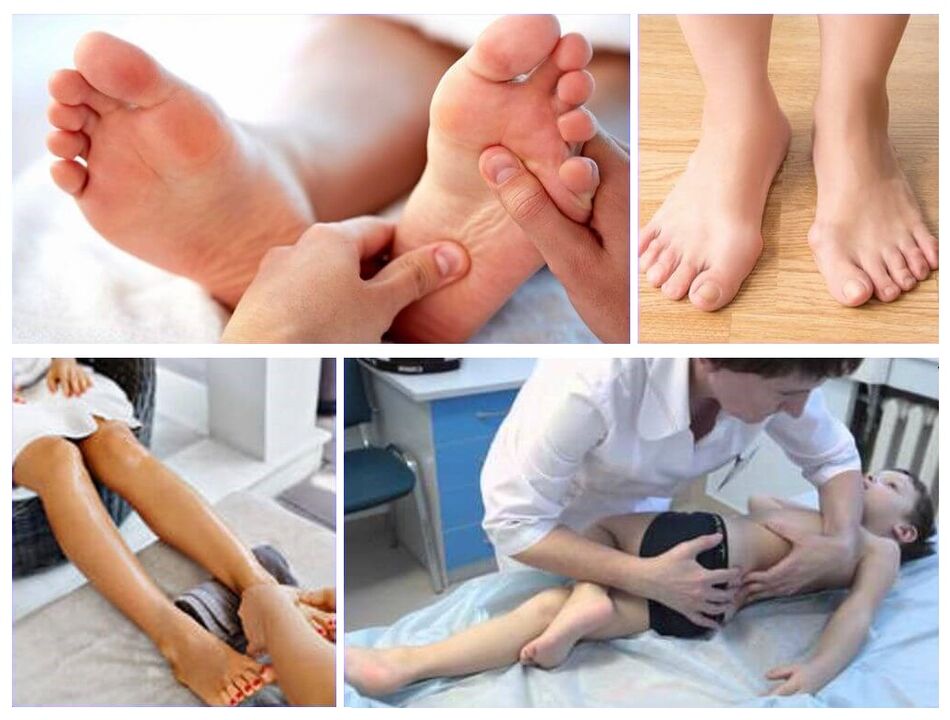
How to treat the valley deformation of the legs in children
Treatment of the valgus deformation of the legs in children is aimed at normalizing the shape of the legs, restoring their functions, and strengthening the ligament and muscle device.In the congenital form of the disease, the orthopedic of children can prescribe plaster binding.Conservative treatment includes the following:
- Night baths.Improve muscle tone, ligaments.To prepare the bath, 1/3 cups of sea salt should be dissolved in 10 liters of warm water.Plant the child into the waist solution for 20 minutes.The meetings are held every other day.One course contains 15 procedures.Repeat treatment every 4 months.
- Massage.Massage with leg deformation in children is one of the most important treatment points.This should be done by a qualified professional.
- Mud and ozotoceros applications.
- Paraffin therapy.Paraffin repulsion is made only on the foot or in the form of a trunk.Heating improves blood circulation, league.
- Acupuncture.
- Electrical stimulation of the muscles of the leg and lower leg.It promotes muscle strengthening.
- Electrophoresis, magnetic therapy.
- Practical therapy.LFK is performed daily with the valgus deformation of the foot.Properly selected exercises can improve the elasticity of the ligaments, muscle strength, increase joint mobility, normalize tissue metabolism and blood circulation.
To correct the valgus deformation of the legs, children should wear special shoes, which have to use unique functional insoles by hardening heels and legs.As far as sport is concerned, it can cycle with the Valgus disorder and swim.
In extreme cases (7%), the disease turns to surgical treatment if all conservative medical measures are ineffective.Can be:
- Artrodesis operations.Enter the still joint of the heel and talus bones, which cause the inner arc muscles to increase.
- Surgical intervention.The manual correction of the child's stop is performed and the plaster places on top of each other.The meetings are held once a week.After each, the foot changes its position.The doctor applies the gypsum to the entire foot (starting from the middle third of the thigh).However, the knee is bent at a ninety degree angle.In the last seat, the doctor fixes the talus-navicular joint in the right position, introducing the Kirschner knitting needle on the skin.Then he dresses gypsum for two months.
- Children who have undergone surgery while treating the leg deformation should always wear special orthopedics that support the arches of the legs.
- Small invasive operations that change the angle between the bones of the foot, which causes the voltage of the ligament device.
Hazard
If the degree of deformation is mild, complete healing is possible.Severe deformation is a serious cosmetic error.The disease causes severe functional damage limbs, which can lead to disability.
The lack of a knowledgeable treatment of disorder can be caused by:
- flat foot;
- constant pain in the legs;
- osteochondrosis;
- Arthrosis;
- abbreviation for the limbs;
- Violation of posture (skoliosis);
- Deformation of the pelvis, ankle and knee joints.
Risk group
The greatest risk of illness with valgus deformation occurs when parents make their feet early (up to 9 months), buy poor quality shoes, or if the size is chosen incorrectly.In addition, infants with ricks, who are genetic prone to curvature, are also prone to pathology.
Preventing a leg deformation

Preventing the disease contains the following points:
- You should not place the child on your feet for 9 months.
- Excludes the formation of ricks (preventive intake of vitamin D).
- Buy shoes with orthopedic insoles.The background of the child's boots should be 3-4 cm like the heel.The sole has to bow well.A prerequisite is the presence of the supervisor.
- Massage your leg.
In addition, scheduled examination of an orthopedic, surgeon, neurologist should not be ignored.At the age of 1 month, the doctor may diagnose the presence of congenital diseases of the skeleton within 3 and 6 months to exclude the formation of ricks, in one year to assess the amount of joint movements, the spine bends, at 3 years - check the limbs, to measure the limbs.
It is impossible to recover quickly by diagnosing the valgus deformation.Parents will be able to evaluate the first results six months after starting conservative therapy.
This article is published exclusively for cognitive purposes and is not scientific or professional medical council.